BLOG
The Download
Where strategy meets results, and we break down what’s working, what’s next and how to turn data into meaningful growth.
Fresh Thinking for Smarter Marketing

Consumers now spend more time with media than they do sleeping – and short-form video is leading the charge across …

How was your last scroll on your social media app of choice? Did you have a quick, efficient trip through …

Is your website holding you back? Learn how it shapes your reputation, attracts the right leads and drives lasting success.
Instagram just dropped some major insights into how their algorithm will work in 2025, and we’re here to break it …
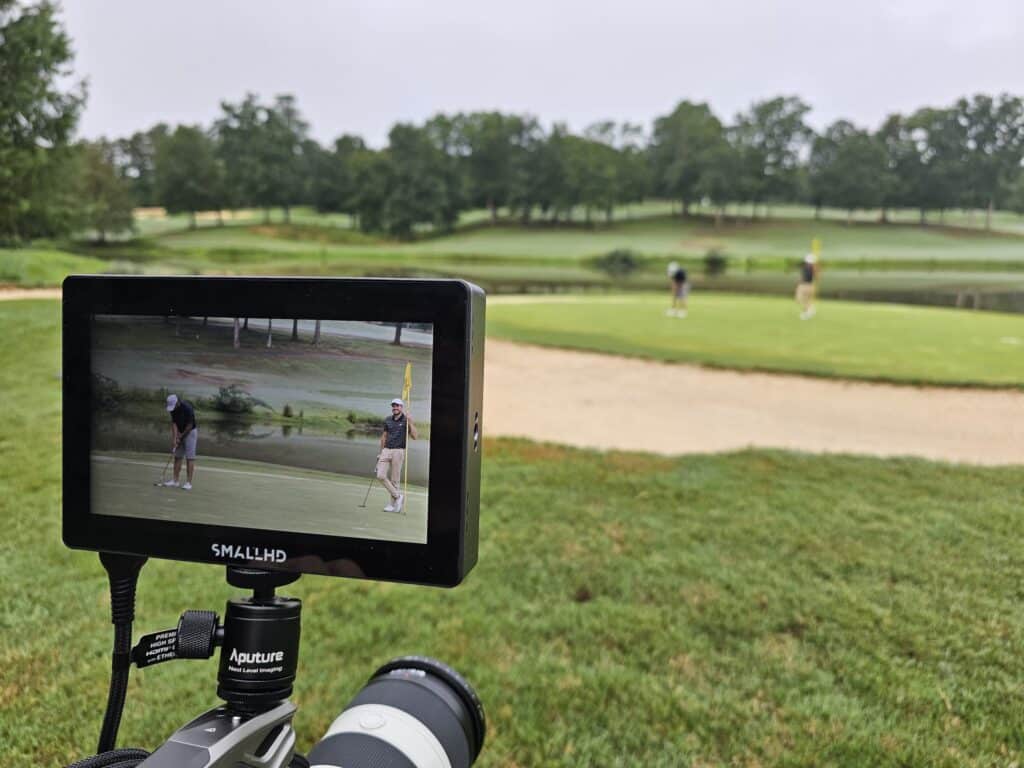

Video, like golf, is a masterclass in strategy and precision. And just like in your digital marketing, every swing counts. …
The future of TikTok in the United States hangs by a thread as the Supreme Court appears inclined to uphold …
Browse by Category
Performance Marketing
Where strategy meets measurable impact. Here, we dive into data-driven tactics that drive real results—leads, conversions, ROI.
Our Work
See what happens when strategy meets execution. Our case studies highlight the impact of smart marketing, sharp ideas and measurable growth.








